Abstract
Background
Catheter-based renal sympathetic denervation (RDN) can reduce sympathetic activity and blood pressure (BP) in patients with hypertension. The present study aimed at investigating the effects of RDN on heart rate (HR), number of premature captions, and heart rate variability (HRV).
Methods
A total of 105 patients (67% male, age 63.5 ± 10 years) with resistant hypertension (BP 169 ± 22/89 ± 14 mmHg) underwent bilateral RDN using a radiofrequency catheter (Symplicity Flex, Medtronic). 24-h Holter monitoring was performed at baseline and after 6 months. Besides HR profile, the number of premature atrial (PAC) and ventricular captions (PVC), time and frequency domain-based HRV were analyzed. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation or median (interquartile range).
Results
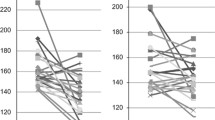
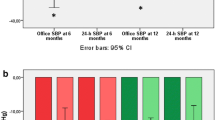
Office systolic and diastolic BP were reduced after RDN by 21.8 ± 25.2 mmHg and 8 ± 18.7 mmHg (p < 0.001 for both), respectively. Twenty-eight (27%) patients had a reduction of < 10 mmHg in systolic BP. At baseline, mean 24-h HR was 65.7 ± 9.9 bpm. The prevalence of PAC [median 1.2 (0.3–6.2)] and PVC [median 1.2 (0.1–13.9)] was low and values of HRV were within normal limits and not different between responders and non-responders. After 6 months, patients with a baseline HR > 72 min had a significant reduction in HR by 2.3 ± 7.1 bpm. Parameters of HRV did not significantly change during follow-up. In patients with ≥ 6 PAC per hour at baseline, a significant median reduction of − 12.4 (− 37.4 to − 2.3) PAC after 6 months was documented (p = 0.002), which occurred independently from BP effects. The number of PVC was not significantly altered after RDN.
Conclusion
In patients with resistant hypertension and elevated HR or high burden of PACs, RDN was associated with a reduction of HR and number of PAC. Parameters of HRV were not changed after RDN nor were predictive of response to RDN.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Böhm M, Linz D, Ukena C, Esler M, Mahfoud F (2014) Renal denervation for the treatment of cardiovascular high risk-hypertension or beyond? Circ Res 115:400–409
Schroeder EB, Liao D, Chambless LE, Prineas RJ, Evans GW, Heiss G (2003) Hypertension, blood pressure, and heart rate variability: the atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study. Hypertension 42:1106–1111
Eckberg DL (1997) Sympathovagal balance: a critical appraisal. Circulation 96:3224–3232
Krum H, Schlaich M, Whitbourn R, Sobotka PA, Sadowski J, Bartus K et al (2009) Catheter-based renal sympathetic denervation for resistant hypertension: a multicentre safety and proof-of-principle cohort study. Lancet 373:1275–1281
Schlaich MP, Sobotka PA, Krum H, Lambert E, Esler MD (2009) Renal sympathetic-nerve ablation for uncontrolled hypertension. New Engl J Med 361:932–934
Hering D, Lambert EA, Marusic P, Walton AS, Krum H, Lambert GW et al (2013) Substantial reduction in single sympathetic nerve firing after renal denervation in patients with resistant hypertension. Hypertension 61:457–464
Grassi G, Seravalle G, Brambilla G, Trabattoni D, Cuspidi C, Corso R et al (2015) Blood pressure responses to renal denervation precede and are independent of the sympathetic and baroreflex effects. Hypertension 65:1209–1216
Ukena C, Mahfoud F, Spies A, Kindermann I, Linz D, Cremers B et al (2013) Effects of renal sympathetic denervation on heart rate and atrioventricular conduction in patients with resistant hypertension. Int J Cardiol 167:2846–2851
Böhm M, Mahfoud F, Townsend RR, Kandzari DE, Pocock S, Ukena C et al (2019) Ambulatory heart rate reduction after catheter-based renal denervation in hypertensive patients not receiving anti-hypertensive medications: data from SPYRAL HTN-OFF MED, a randomized, sham-controlled, proof-of-concept trial. Eur Heart J 40:743–751
Linz D, Mahfoud F, Schotten U, Ukena C, Hohl M, Neuberger HR et al (2013) Renal sympathetic denervation provides ventricular rate control but does not prevent atrial electrical remodeling during atrial fibrillation. Hypertension 61:225–231
Tsioufis C, Papademetriou V, Tsiachris D, Dimitriadis K, Kasiakogias A, Kordalis A et al (2014) Drug-resistant hypertensive patients responding to multielectrode renal denervation exhibit improved heart rate dynamics and reduced arrhythmia burden. J Hum Hypertens 28:587–593
Ukena C, Bauer A, Mahfoud F, Schreieck J, Neuberger HR, Eick C et al (2012) Renal sympathetic denervation for treatment of electrical storm: first-in-man experience. Clin Res Cardiol 101:63–67
Mahfoud F, Schlaich M, Kindermann I, Ukena C, Cremers B, Brandt MC et al (2011) Effect of renal sympathetic denervation on glucose metabolism in patients with resistant hypertension: a pilot study. Circulation 123:1940–1946
Heart rate variability (1996) Standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use. Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Eur Heart J 17:354–381
Townsend RR, Mahfoud F, Kandzari DE, Kario K, Pocock S, Weber MA et al (2017) Catheter-based renal denervation in patients with uncontrolled hypertension in the absence of antihypertensive medications (SPYRAL HTN-OFF MED): a randomised, sham-controlled, proof-of-concept trial. Lancet 390:2160–2170
Azizi M, Schmieder RE, Mahfoud F, Weber MA, Daemen J, Davies J et al (2018) Endovascular ultrasound renal denervation to treat hypertension (RADIANCE-HTN SOLO): a multicentre, international, single-blind, randomised, sham-controlled trial. Lancet 391:2335–2345
Kandzari DE, Böhm M, Mahfoud F, Townsend RR, Weber MA, Pocock S et al (2018) Effect of renal denervation on blood pressure in the presence of antihypertensive drugs: 6-month efficacy and safety results from the SPYRAL HTN-ON MED proof-of-concept randomised trial. Lancet 391:2346–2355
Mahfoud F, Böhm M, Azizi M, Pathak A, Durand Zaleski I, Ewen S et al (2015) Proceedings from the European clinical consensus conference for renal denervation: considerations on future clinical trial design. Eur Heart J 36:2219–2227
Lüscher TF, Mahfoud F (2014) Renal nerve ablation after SYMPLICITY HTN-3: confused at the higher level? Eur Heart. J 35:1706–1711
Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, Agabiti Rosei E, Azizi M, Burnier M et al (2018) ESC/ESH guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J 39:3021–3104
Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, Bueno H, Cleland JGF, Coats AJS et al (2016) ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: The Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J 37:2129–2200
Levy MN, Zieske H (1969) Autonomic control of cardiac pacemaker activity and atrioventricular transmission. J Appl Physiol 27:465–470
Böhm M, Ukena C, Ewen S, Linz D, Zivanovic I, Hoppe U et al (2016) Renal denervation reduces office and ambulatory heart rate in patients with uncontrolled hypertension: 12-month outcomes from the global SYMPLICITY registry. J Hypertens 34:2480–2486
Kannel WB, Wolf PA, Benjamin EJ, Levy D (1998) Prevalence, incidence, prognosis, and predisposing conditions for atrial fibrillation: population-based estimates. Am J Cardiol 82:2N–9N
Schneider MP, Hua TA, Bohm M, Wachtell K, Kjeldsen SE, Schmieder RE (2010) Prevention of atrial fibrillation by Renin-Angiotensin system inhibition a meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 55:2299–2307
Iwasaki YK, Nishida K, Kato T, Nattel S (2011) Atrial fibrillation pathophysiology: implications for management. Circulation 124:2264–2274
Binici Z, Intzilakis T, Nielsen OW, Kober L, Sajadieh A (2010) Excessive supraventricular ectopic activity and increased risk of atrial fibrillation and stroke. Circulation 121:1904–1911
Larsen BS, Kumarathurai P, Falkenberg J, Nielsen OW, Sajadieh A (2015) Excessive Atrial Ectopy and Short Atrial Runs Increase the Risk of Stroke Beyond Incident Atrial Fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol 66:232–241
Pokushalov E, Romanov A, Corbucci G, Artyomenko S, Baranova V, Turov A et al (2012) A randomized comparison of pulmonary vein isolation with versus without concomitant renal artery denervation in patients with refractory symptomatic atrial fibrillation and resistant hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 60:1163–1170
Pokushalov E, Romanov A, Katritsis DG, Artyomenko S, Bayramova S, Losik D et al (2014) Renal denervation for improving outcomes of catheter ablation in patients with atrial fibrillation and hypertension: early experience. Heart Rhythm 11:1131–1138
Romanov A, Pokushalov E, Ponomarev D, Strelnikov A, Shabanov V, Losik D, et al (2017) Pulmonary vein isolation with concomitant renal artery denervation is associated with reduction in both arterial blood pressure and atrial fibrillation burden: data from implantable cardiac monitor. Cardiovasc Therap 35.
Kiuchi MG, Chen S, Hoye NA, Purerfellner H (2018) Pulmonary vein isolation combined with spironolactone or renal sympathetic denervation in patients with chronic kidney disease, uncontrolled hypertension, paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, and a pacemaker. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 51:51–59
Feyz L, Theuns DA, Bhagwandien R, Strachinaru M, Kardys I, Van Mieghem NM et al (2019) Atrial fibrillation reduction by renal sympathetic denervation: 12 months' results of the AFFORD study. Clin Res Cardiol 108:634–642
de Jong MR, Hoogerwaard AF, Adiyaman A, Smit JJJ, Ramdat Misier AR, Heeg JE et al (2018) Treatment of atrial fibrillation in patients with enhanced sympathetic tone by pulmonary vein isolation or pulmonary vein isolation and renal artery denervation: clinical background and study design : The ASAF trial: ablation of sympathetic atrial fibrillation. Clin Res Cardiol 107:539–547
Sassi R, Cerutti S, Lombardi F, Malik M, Huikuri HV, Peng CK et al (2015) Advances in heart rate variability signal analysis: joint position statement by the e-Cardiology ESC Working Group and the European Heart Rhythm Association co-endorsed by the Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society. Europace 17:1341–1353
Peters CD, Mathiassen ON, Vase H, Bech Norgaard J, Christensen KL, Schroeder AP et al (2017) The effect of renal denervation on arterial stiffness, central blood pressure and heart rate variability in treatment resistant essential hypertension: a substudy of a randomized sham-controlled double-blinded trial (the ReSET trial). Blood Press 26:366–380
Verloop WL, Spiering W, Vink EE, Beeftink MM, Blankestijn PJ, Doevendans PA et al (2015) Denervation of the renal arteries in metabolic syndrome: the DREAMS-study. Hypertension 65:751–757
Hoogerwaard AF, de Jong MR, Adiyaman A, Smit JJJ, Delnoy P, Heeg JE et al (2019) Renal sympathetic denervation induces changes in heart rate variability and is associated with a lower sympathetic tone. Clin Res Cardiol 108:22–30
Tzafriri AR, Mahfoud F, Keating JH, Markham PM, Spognardi A, Wong G et al (2014) Innervation patterns may limit response to endovascular renal denervation. J Am Coll Cardiol 64:1079–1087
Mahfoud F, Tunev S, Ewen S, Cremers B, Ruwart J, Schulz-Jander D et al (2015) Impact of lesion placement on efficacy and safety of catheter-based radiofrequency renal denervation. J Am Coll Cardiol 66:1766–1775
Acknowledgements
CU, FM, and MB are supported by the Ministry of Science and Economy of the Saarland. FM is supported by the Deutsche Hochdruckliga. MB and FM are supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Transregio-SFB 219). All authors except TS received scientific support and speaker honorarium from Medtronic©. The authors would like to thank Irmgard Kiefer for excellent technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ukena, C., Seidel, T., Rizas, K. et al. Effects of renal denervation on 24-h heart rate and heart rate variability in resistant hypertension. Clin Res Cardiol 109, 581–588 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-019-01543-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-019-01543-6