Abstract
Aims
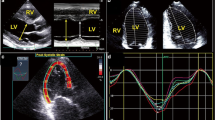
The electrocardiographic pattern of early repolarization (ER) is related to increased cardiac mortality in the general population. The pathophysiological basis of ER is largely unknown. We investigated the association of echocardiographic structural and functional parameters of the left ventricle with the presence of ER in the community.
Methods and results
The presence of ER (ER+) was assessed in 13,878 participants (mean age 54.6 years, 51.1% women) of the Gutenberg Health Study and related to left ventricular structure and function derived from standard echocardiography. The prevalence of ER was 5.0% (694/13,878), with higher prevalence in men than women (6.6% vs. 3.5%, p < 0.001). In men baseline characteristics differed including a lower BMI and a lower heart rate in ER+ individuals, whereas in women there were only minor differences. Multivariable-adjusted logistic regression analysis in men showed an association of ER with smaller diameters (left-ventricular end-diastolic diameter: OR 0.77 95% CI 0.69–0.86, p < 0.001; left-ventricular end-systolic diameter: OR 0.86 95% CI 0.78–0.95, p = 0.0035), and lower left-ventricular end-diastolic and end-systolic volume (OR 0.72 95% CI 0.65, 0.80, p < 0.001 and OR 0.80 95% CI 0.72, 0.89, p < 0.001). In women, the associations of ER with left ventricular diameters and volumes showed a similar direction, but were not as pronounced.
Conclusion
In the community, the ER pattern predominantly occurs in men with a low heart rate and a slender habit. Furthermore, ER is not associated with higher left ventricular mass or size but rather with smaller left ventricular diameters and volumes with a regular systolic and diastolic function. Patterns were comparable in women, but less strong.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haissaguerre M, Derval N, Sacher F, Jesel L, Deisenhofer I, de Roy L, Pasquie JL, Nogami A, Babuty D, Yli-Mayry S, De Chillou C, Scanu P, Mabo P, Matsuo S, Probst V, Le Scouarnec S, Defaye P, Schlaepfer J, Rostock T, Lacroix D, Lamaison D, Lavergne T, Aizawa Y, Englund A, Anselme F, O’Neill M, Hocini M, Lim KT, Knecht S, Veenhuyzen GD, Bordachar P, Chauvin M, Jais P, Coureau G, Chene G, Klein GJ, Clementy J (2008) Sudden cardiac arrest associated with early repolarization. N Engl J Med 358(19):2016–2023
Tikkanen JT, Anttonen O, Junttila MJ, Aro AL, Kerola T, Rissanen HA, Reunanen A, Huikuri HV (2009) Long-term outcome associated with early repolarization on electrocardiography. N Engl J Med 361(26):2529–2537
Rosso R, Kogan E, Belhassen B, Rozovski U, Scheinman MM, Zeltser D, Halkin A, Steinvil A, Heller K, Glikson M, Katz A, Viskin S (2008) J-point elevation in survivors of primary ventricular fibrillation and matched control subjects: incidence and clinical significance. J Am Coll Cardiol 52(15):1231–1238
Sinner MF, Reinhard W, Muller M, Beckmann BM, Martens E, Perz S, Pfeufer A, Winogradow J, Stark K, Meisinger C, Wichmann HE, Peters A, Riegger GA, Steinbeck G, Hengstenberg C, Kaab S (2010) Association of early repolarization pattern on ECG with risk of cardiac and all-cause mortality: a population-based prospective cohort study (MONICA/KORA). PLoS Med 7(7):e1000314
Noseworthy PA, Tikkanen JT, Porthan K, Oikarinen L, Pietila A, Harald K, Peloso GM, Merchant FM, Jula A, Vaananen H, Hwang SJ, O’Donnell CJ, Salomaa V, Newton-Cheh C, Huikuri HV (2011) The early repolarization pattern in the general population: clinical correlates and heritability. J Am Coll Cardiol 57(22):2284–2289
Uberoi A, Jain NA, Perez M, Weinkopff A, Ashley E, Hadley D, Turakhia MP, Froelicher V (2011) Early repolarization in an ambulatory clinical population. Circulation 124(20):2208–2214
Junttila MJ, Tikkanen JT, Kentta T, Anttonen O, Aro AL, Porthan K, Kerola T, Rissanen HA, Knekt P, Huikuri HV (2014) Early repolarization as a predictor of arrhythmic and nonarrhythmic cardiac events in middle-aged subjects. Heart Rhythm 11(10):1701–1706
Cheng YJ, Lin XX, Ji CC, Chen XM, Liu LJ, Tang K, Wu SH (2016) Role of early repolarization pattern in increasing risk of death. J Am Heart Assoc 5:(9)
Tikkanen JT, Junttila MJ, Anttonen O, Aro AL, Luttinen S, Kerola T, Sager SJ, Rissanen HA, Myerburg RJ, Reunanen A, Huikuri HV (2011) Early repolarization: electrocardiographic phenotypes associated with favorable long-term outcome. Circulation 123(23):2666–2673
Quattrini FM, Pelliccia A, Assorgi R, DiPaolo FM, Squeo MR, Culasso F, Castelli V, Link MS, Maron BJ (2014) Benign clinical significance of J-wave pattern (early repolarization) in highly trained athletes. Heart Rhythm 11(11):1974–1982
Stumpf C, Simon M, Wilhelm M, Zimmermann S, Rost C, Achenbach S, Brem MH (2016) Left atrial remodeling, early repolarization pattern, and inflammatory cytokines in professional soccer players. J Cardiol 68(1):64–70
Noseworthy PA, Weiner R, Kim J, Keelara V, Wang F, Berkstresser B, Wood MJ, Wang TJ, Picard MH, Hutter AM Jr, Newton-Cheh C, Baggish AL (2011) Early repolarization pattern in competitive athletes: clinical correlates and the effects of exercise training. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 4(4):432–440
Wild PS, Sinning CR, Roth A, Wilde S, Schnabel RB, Lubos E, Zeller T, Keller T, Lackner KJ, Blettner M, Vasan RS, Munzel T, Blankenberg S (2010) Distribution and categorization of left ventricular measurements in the general population: results from the population-based Gutenberg Heart Study. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 3(5):604–613
Lang RM, Bierig M, Devereux RB, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Pellikka PA, Picard MH, Roman MJ, Seward J, Shanewise J, Solomon S, Spencer KT, St John Sutton M, Stewart W, American Society of Echocardiography’s N, Standards C, Task Force on Chamber Q, American College of Cardiology Echocardiography C, American Heart A, European Association of Echocardiography ESoC (2006) Recommendations for chamber quantification. Eur J Echocardiogr 7(2):79–108
Lang RM, Badano LP, Mor-Avi V, Afilalo J, Armstrong A, Ernande L, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Goldstein SA, Kuznetsova T, Lancellotti P, Muraru D, Picard MH, Rietzschel ER, Rudski L, Spencer KT, Tsang W, Voigt JU (2015) Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: an update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 16(3):233–270
Devereux RB, Alonso DR, Lutas EM, Gottlieb GJ, Campo E, Sachs I, Reichek N (1986) Echocardiographic assessment of left ventricular hypertrophy: comparison to necropsy findings. Am J Cardiol 57(6):450–458
Macfarlane PW, Antzelevitch C, Haissaguerre M, Huikuri HV, Potse M, Rosso R, Sacher F, Tikkanen JT, Wellens H, Yan GX (2015) The early repolarization pattern: a consensus paper. J Am Coll Cardiol 66(4):470–477
Figueiras A, Domenech-Massons JM, Cadarso C (1998) Regression models: calculating the confidence interval of effects in the presence of interactions. Stat Med 17(18):2099–2105
O’Neal WT, Wang YG, Wu HT, Zhang ZM, Li Y, Tereshchenko LG, Estes EH, Daubechies I, Soliman EZ (2016) Electrocardiographic J wave and cardiovascular outcomes in the general population (from the atherosclerosis risk in communities study). Am J Cardiol 118(6):811–815
Serra-Grima R, Donate M, Alvarez-Garcia J, Barradas-Pires A, Ferrero A, Carballeira L, Puig T, Rodriguez E, Cinca J (2015) Long-term follow-up of early repolarization pattern in elite athletes. Am J Med 128(2):192 e191–e199
Reinhard W, Trenkwalder T, Haller B, Meindl C, Schoenfeld J, Kaess BM, Hengstenberg C, Schunkert H, Pressler A, Halle M, Scherr J (2018) The early repolarization pattern: echocardiographic characteristics in elite athletes. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/anec.12617
Gulel O, Dagasan G, Yuksel S, Soylu K, Sahin M (2016) Evaluation of left ventricular myocardial deformation parameters in individuals with electrocardiographic early repolarization pattern. Anatol J Cardiol 16(11):850–854
McNamara DA, Benett A, Berry JD, Link MS (2018) Abstract P026: early repolarization pattern is associated with increased left ventricular mass and left ventricular hypertrophy: results from the Dallas heart study. Circulation 137(No.suppl_1):AP026
Drazner MH, Dries DL, Peshock RM, Cooper RS, Klassen C, Kazi F, Willett D, Victor RG (2005) Left ventricular hypertrophy is more prevalent in blacks than whites in the general population: the Dallas Heart Study. Hypertension 46(1):124–129
Stevens J, Cai J, Pamuk ER, Williamson DF, Thun MJ, Wood JL (1998) The effect of age on the association between body-mass index and mortality. N Engl J Med 338(1):1–7
Zhang D, Shen X, Qi X (2016) Resting heart rate and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in the general population: a meta-analysis. CMAJ 188(3):E53–E63
Mercer BN, Begg GA, Page SP, Bennett CP, Tayebjee MH, Mahida S (2016) Early repolarization syndrome; mechanistic theories and clinical correlates. Front Physiol 7:266
Chauveau S, Janin A, Till M, Morel E, Chevalier P, Millat G (2017) Early repolarization syndrome caused by de novo duplication of KCND3 detected by next-generation sequencing. HeartRhythm Case Rep 3(12):574–578
Walsh JA 3rd, Ilkhanoff L, Soliman EZ, Prineas R, Liu K, Ning H, Lloyd-Jones DM (2013) Natural history of the early repolarization pattern in a biracial cohort: CARDIA (Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults) Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 61(8):863–869
Chau K, Girerd N, Magnusson M, Lamiral Z, Bozec E, Merckle L, Leosdottir M, Bachus E, Frikha Z, Ferreira JP, Despres JP, Rossignol P, Boivin JM, Zannad F (2018) Obesity and metabolic features associated with long-term developing diastolic dysfunction in an initially healthy population-based cohort. Clin Res Cardiol 107(10):887–896
Maufrais C, Doucende G, Rupp T, Dauzat M, Obert P, Nottin S, Schuster I (2017) Left ventricles of aging athletes: better untwisters but not more relaxed during exercise. Clin Res Cardiol 106(11):884–892
Catalano O, Antonaci S, Moro G, Mussida M, Frascaroli M, Baldi M, Cobelli F, Baiardi P, Nastoli J, Bloise R, Monteforte N, Napolitano C, Priori SG (2009) Magnetic resonance investigations in Brugada syndrome reveal unexpectedly high rate of structural abnormalities. Eur Heart J 30(18):2241–2248
Buckert D, Cieslik M, Tibi R, Radermacher M, Rasche V, Bernhardt P, Hombach V, Rottbauer W, Wohrle J (2018) Longitudinal strain assessed by cardiac magnetic resonance correlates to hemodynamic findings in patients with severe aortic stenosis and predicts positive remodeling after transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Clin Res Cardiol 107(1):20–29
Chua HC, Servatius H, Asatryan B, Schaller A, Rieubland C, Noti F, Seiler J, Roten L, Baldinger SH, Tanner H, Fuhrer J, Haeberlin A, Lam A, Pless SA, Medeiros-Domingo A (2018) Unexplained cardiac arrest: a tale of conflicting interpretations of KCNQ1 genetic test results. Clin Res Cardiol 107(8):670–678
Biering-Sorensen T, Biering-Sorensen SR, Olsen FJ, Sengelov M, Jorgensen PG, Mogelvang R, Shah AM, Jensen JS (2017) Global longitudinal strain by echocardiography predicts long-term risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in a low-risk general population: the Copenhagen city heart study. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 10(3):e005521
Acknowledgements
The Gutenberg Health Study is funded through the government of Rhineland-Palatinate (“Stiftung Rheinland-Pfalz für Innovation”, contract AZ 961-386261/733), the research programs “Wissen schafft Zukunft” and “Center for Translational Vascular Biology (CTVB)” of the Johannes Gutenberg-University of Mainz, and its contract with Boehringer Ingelheim and PHILIPS Medical Systems, including an unrestricted grant for the Gutenberg Health Study. Philipp S. Wild is funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF 01EO1503) and he is PI of the German Center for Cardiovascular Research (DZHK). We thank all study participants for their willingness to provide data for this research project and we are indebted to all coworkers for their enthusiastic commitment. This project has received funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (grant agreement No 648131) (RBS) and German Research Foundation Emmy Noether Programme (SCHN 1149/3-1) (RBS). This work was performed in the context of the Junior Research Alliance symAtrial project funded by the German Ministry of Research and Education (BMBF 01ZX1408A) e:Med—Systems Medicine program (RBS, TZ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trenkwalder, T., Rübsamen, N., Schmitt, V.H. et al. Left ventricular geometry and function in early repolarization: results from the population-based Gutenberg Health Study. Clin Res Cardiol 108, 1107–1116 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-019-01445-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-019-01445-7